Guinea, officially known as the Republic of Guinea, is a West African country that boasts a rich history, diverse culture, and a landscape that extends from coastal plains to mountainous regions. The country is known for its unique geographical features including the Guinea Highlands, the Niger River and the Atlantic coastline. In this article, we will highlight the details of the Guinea map, its major geographical elements and their importance to the nation.
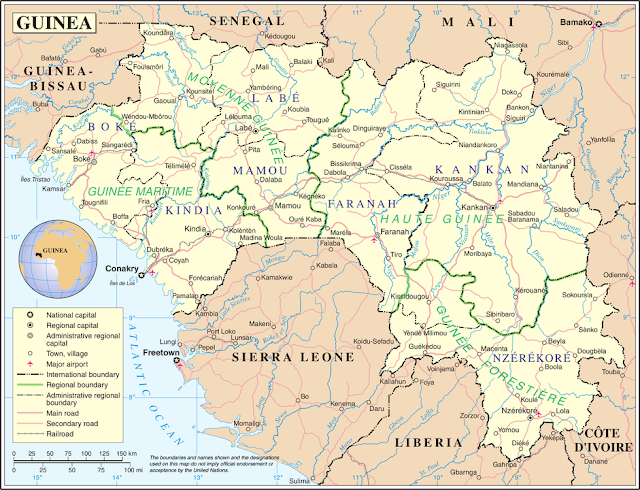
Guinea map
Geographical situation:
Located on the west coast of Africa, Guinea is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia and Sierra Leone. The Atlantic Ocean borders the country to the west, giving Guinea about 320 kilometers of coastline.
Physical features:
- Guinea Highlands: One of the most prominent features on a Guinea map is the Guinea Highlands, a mountainous region that covers most of the central and eastern parts of the country. This high terrain is characterized by peaks, plateaus and deep valleys, which offer breathtaking views. The Fouta Djelloun Plateau, with its beautiful landscapes and waterfalls, is a notable attraction of the Guinean Highlands.
- Niger River: The Niger River, one of Africa's major waterways, flows through Guinea's southeastern region. The river plays an important role in the geography of the country, providing water resources for agriculture, transportation and supporting diverse ecosystems along its banks.
- Coastal Plains: Guinea's coastal plains stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, dotted with mangrove swamps and estuaries. The capital city, Conakry, is located on the Cape Varga Peninsula and serves as an important port city.
- Mangrove Forest: The coastal areas are home to extensive mangrove forests, which act as important ecosystems that support a variety of marine life. These mangroves play a role in protecting the coastline from erosion and provide habitat for diverse flora and fauna.
Cultural importance:
Guinea's geographical diversity has a profound impact on its cultural landscape. For example, the Fouta Djelloun Plateau is not only a geographical wonder, but also home to various ethnic groups, each of which contributes to the country's cultural mosaic. The rivers and coastal areas have influenced traditional fishing practices and provided a source of livelihood for coastal communities.
Economic Importance:
- Agriculture: The fertile land in the Guinean Highlands is conducive to agriculture, and the region is known for the cultivation of crops such as rice, millet, and maize. The Niger River basin also supports agriculture through irrigation.
- Digging: Guinea is endowed with rich mineral resources, and mining plays an important role in its economy. Bauxite, an aluminum ore, is a major export product, and the country has significant reserves of iron ore, diamonds, and gold.
The Guinea map is a testament to the country's diverse geography, which has shaped its culture, economy and lifestyle. From the Guinean highlands to the coastal plains and river valleys, each region makes a unique contribution to the country's identity. As Guinea continues to develop and progress, its geographical characteristics will undoubtedly play an important role in shaping its future.
Some interesting facts about Guinea are:
- Capital and largest city: The capital of Guinea is Conakry, which is also the country's largest city. It is situated on the Atlantic coast.
- Official language: The official language of Guinea is French, a legacy of its colonial history. However, many indigenous languages are spoken throughout the country, reflecting its diverse ethnic groups.
- Independence: Guinea gained independence from French colonial rule on October 2, 1958. Sékou Touré became the first President of the newly independent nation.
- Geography: Guinea is located in West Africa and is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia and Sierra Leone. Its geography is diverse including the Guinean Highlands, coastal plains and the Niger River.
- Guinea Highlands: The Fouta Djelloun Plateau, part of the Guinean Highlands, is an important geographical feature. It is known for its beautiful landscapes, waterfalls and the source of several major rivers.
- Natural resources: Guinea is rich in natural resources. It is one of the world's largest producers of bauxite, an important source of aluminium. The country also has important reserves of iron ore, diamonds, gold and other minerals.
- Niger River: The Niger River, one of the major rivers of Africa, flows through the southeastern part of Guinea. It plays an important role in the country's agriculture, providing water for irrigation and supporting diverse ecosystems.
- Cultural diversity: Guinea is home to a variety of ethnic groups, each with their own unique traditions, languages, and cultural practices. Major ethnic groups include the Fula, Malinke and Susu.
- Music and dance: Guinea is famous for its vibrant music and dance traditions. The country has produced internationally acclaimed musicians and dancers and traditional music plays an important role in cultural celebrations.
- Tourist Attractions: Visitors to Guinea can explore the beautiful landscapes of the Fouta Djallon Plateau, visit the beautiful Les Cascades de la Soumba waterfalls, and experience the vibrant markets and culture in Conakry.
- Political History: Guinea was the first French West African colony to gain independence. The country's first President Sékou Touré led Guinea with a policy of non-alignment during the Cold War.
- Wildlife: Guinea is home to diverse wildlife, including chimpanzees, elephants, hippos, and various species of monkeys. The country has national parks and reserves that aim to preserve its rich biodiversity.
Comments
Post a Comment